1 min to read
Seq2Seq

最简单的描述
Seq2Seq的简单描述就是将一段Seq编码为定长的向量,然后这个定长的向量再解码为一段Seq;如下图:
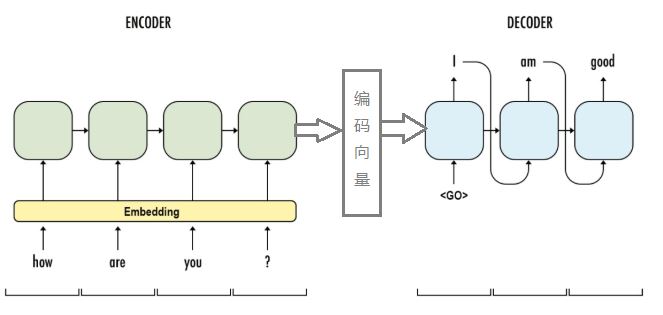
关于编码器和解码器的工作原理
Seq2Seq模型由两部分构成,一部分是编码器,另一部分是解码器;
编码器的作用就是将Seq编码为定长的向量,一般通过RNN来实现,与一般模型中的RNN层没有区别;可以将最后时刻的神经元状态作为编码向量。
解码器的作用是将定长向量解码称为一段Seq,仍然通过RNN层来实现,与一般模型RNN层的区别是,在预测的时候,初始化状态是编码向量,第一个时刻输入是
训练的时候对于解码器来说,除了将编码向量作为初始化状态之外,第一时刻的输入是
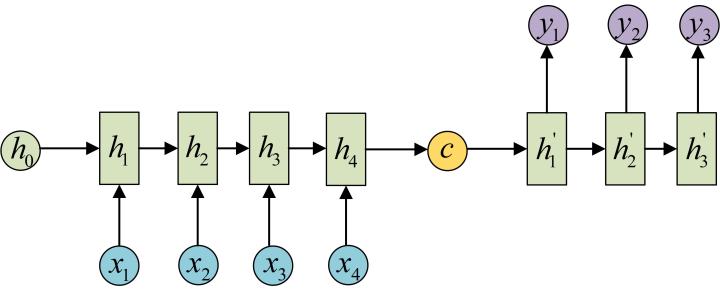
最基础的Seq2Seq网络结构
最简单的基于RNN的Seq2Seq的网络结构如下:
LSTM、多层、多时刻的变种
Seq2Seq有一些变种,比如对于RNN的选择,可以选最基础的RNN,也可以选择LSTM、GRU等
同时也可以是单层或者多层;基于多层RNN的Seq2Seq模型如下图:
基于LSTM的Seq2Seq模型如下:
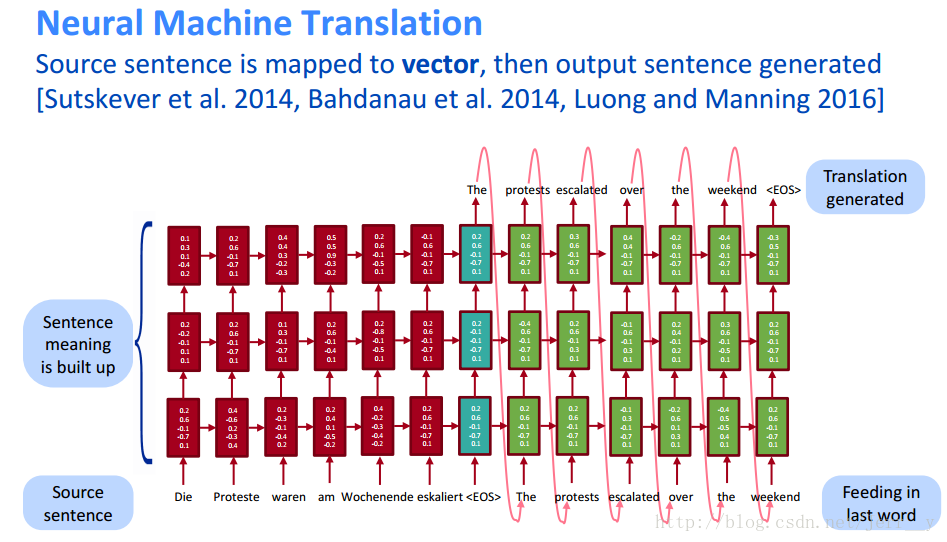
另外的变种做法,将最终的编码向量用于每一时刻的输入,而不是用于初始化状态;此类网络的结构如下图:
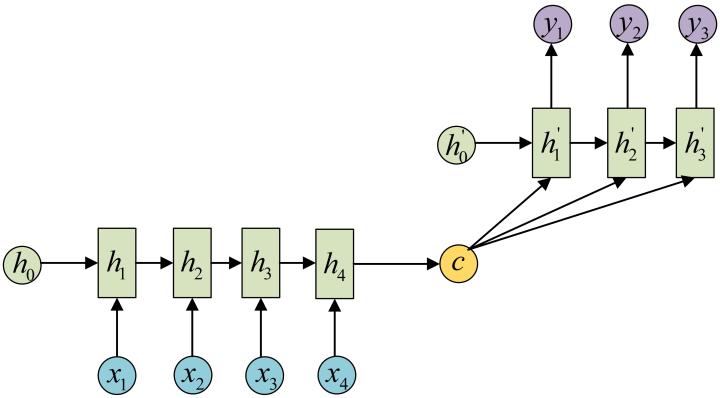
加入Attention机制的变种
Attention机制有很多中,一般分两类,RNN + Attention的使用方式 以及 transformer中的self attention;这两种分别讨论。
RNN + Attention:
Attention机制是基于上面提到的,编码向量用于每一时刻的的输入进行变种而来的。
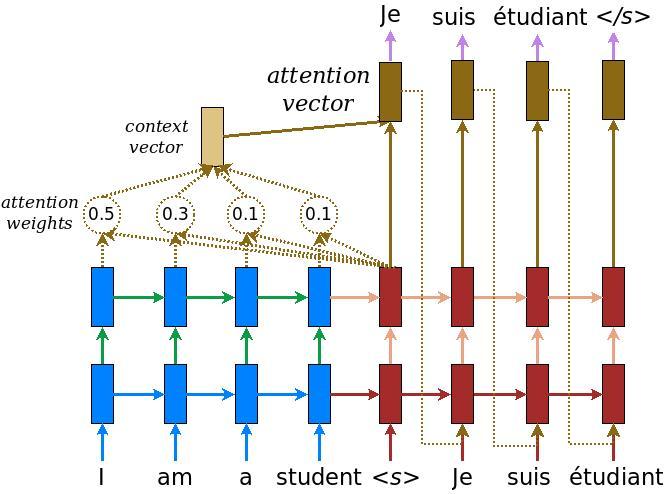
Attention机制将编码器的每一步隐藏状态进行连接,得到一个“语义向量”(一般设置:return_sequences=True);
这个向量在解码的每一步使用不同的权重做一次全连接,然后将全连接之后的输出进行reduce,作为这一时刻的输入。
权重是计算出来的,而不是设置变量训练出来的。计算方式如下:
根据解码时前一个时刻的隐藏状态跟编码每一个时刻的隐藏状态计算dot,然后进行softmax得到seq_length个α值;
有两种类型的attention机制,一种是global,另一种是local (参考论文:Effective Approaches to Attention-based Neural Machine Translation.pdf)
global类型的attention 网络结构如下图:
官方实现:https://www.tensorflow.org/alpha/tutorials/text/nmt_with_attention
local类型的attention是只取encoder的一部分hidden state作为语义向量,并且每一步使用的可能不一样。
transformer中的attention
一般提到self attention 都是transformer中模型中用到的attention。
实现
以上各种Seq2Seq的实现:Seq2Seq
BahdanauAttention的前向传播实现
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.seq2seq import BahdanauAttention, AttentionWrapper, BasicDecoder, TrainingHelper
from tensorflow.contrib.seq2seq.python.ops import decoder
from tensorflow.python.ops.rnn_cell_impl import LSTMCell
seq_length = 6
batch_size = 3
embeding_size = 5
input_data = tf.random_normal(shape=[batch_size, seq_length, embeding_size])
input_label = tf.random_normal(shape=[batch_size, seq_length, 1])
encoder = tf.keras.layers.LSTM(units=2, return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
out_seq, out, state = encoder(input_data)
attention = BahdanauAttention(3, out_seq)
lstm_attention = AttentionWrapper(LSTMCell(num_units=2), attention_mechanism=attention)
helper = TrainingHelper(input_label, tf.constant(seq_length, shape=[batch_size]))
my_decoder = BasicDecoder(lstm_attention,
helper,
initial_state=lstm_attention.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32))
final_outputs, final_state, final_sequence_lengths = decoder.dynamic_decode(my_decoder)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run((tf.local_variables_initializer(), tf.global_variables_initializer()))
print(out_seq.shape)
print(out.shape)
print(state.shape)
(a, b, c) = sess.run((final_outputs, final_state, final_sequence_lengths))
print(a.rnn_output, b, c)

Comments