4 min to read
循环神经网络

循环神经网络特点是可以挖掘出数据序列之间的关系信息,实际使用中每一个样本的输入是数据序列,也就是一系列的数据,其中的每个数据是一个时间步。
RNN
RNN层也是由一个或者多个神经元组成的,每个神经元的输入由两部分构成,一部分是序列数据中的某一个数据,另一部分是这个数据的前一个数据经过循环层神经元时,神经元输出的隐藏状态。神经元的输出也包含两部分,一部分时输出的预测值,另一部分时隐藏状态。RNN的结构图如下:
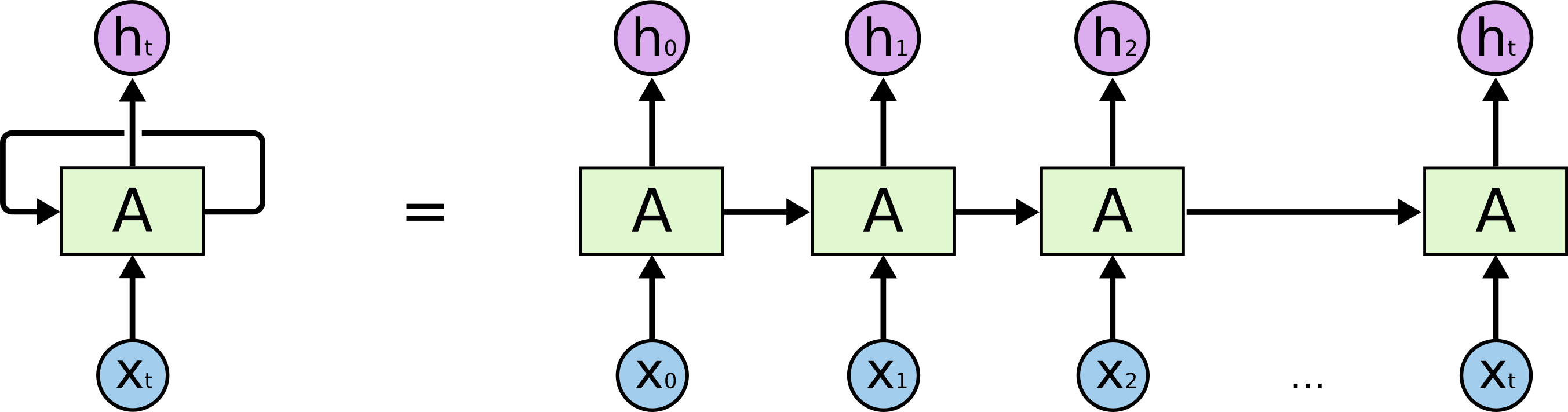
其网络结构与计算过程可从如下Demo中得知:
# coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
tf.enable_eager_execution()
x = np.linspace(-100, 100, 1000)
y = np.sin(x)
time_step = 50
class MinimalRNNCell(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, units, **kwargs):
self.units = units
self.state_size = units
super(MinimalRNNCell, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def build(self, input_shape):
self.kernel = self.add_weight(shape=(input_shape[-1], self.units),
initializer='uniform',
name='kernel')
self.recurrent_kernel = self.add_weight(
shape=(self.units, self.units),
initializer='uniform',
name='recurrent_kernel')
self.built = True
def call(self, inputs, states):
prev_output = states[0]
h = tf.matmul(inputs, self.kernel)
output = h + tf.matmul(prev_output, self.recurrent_kernel)
return output, [output]
def to_train_label(serial, time_step=50):
inputs = []
out = []
for i in range(serial.shape[0] - time_step - 1):
inputs.append(serial[i:i + time_step])
out.append(serial[i + time_step])
return np.array(inputs), np.array(out)
input_data, label = to_train_label(y, time_step)
input_data = tf.expand_dims(input_data, 2)
label = tf.expand_dims(label, 1)
print(input_data.shape, label.shape)
input = tf.keras.Input(shape=[time_step, 1])
cells = MinimalRNNCell(64)
rnn = tf.keras.layers.RNN(cells)(input)
out = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=1)(rnn)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=input, outputs=out)
model.compile(optimizer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(), loss='mean_squared_error')
model.fit(input_data, label, batch_size=512, epochs=100)
start = np.expand_dims(input_data.numpy()[-1], 0).copy()
pres = []
for i in range(50):
next = model.predict(start)
start[0, :time_step - 1] = start[0, 1:]
start[0, time_step - 1] = next
pres.append(next[0][0])
last = np.ndarray.flatten(input_data.numpy()[-1])
all = np.concatenate((last, pres))
plt.plot(list(range(len(all))), all)
plt.show()
print(all)
自定义RNN神经元:https://keras.io/zh/layers/recurrent/
RNN的反向传播
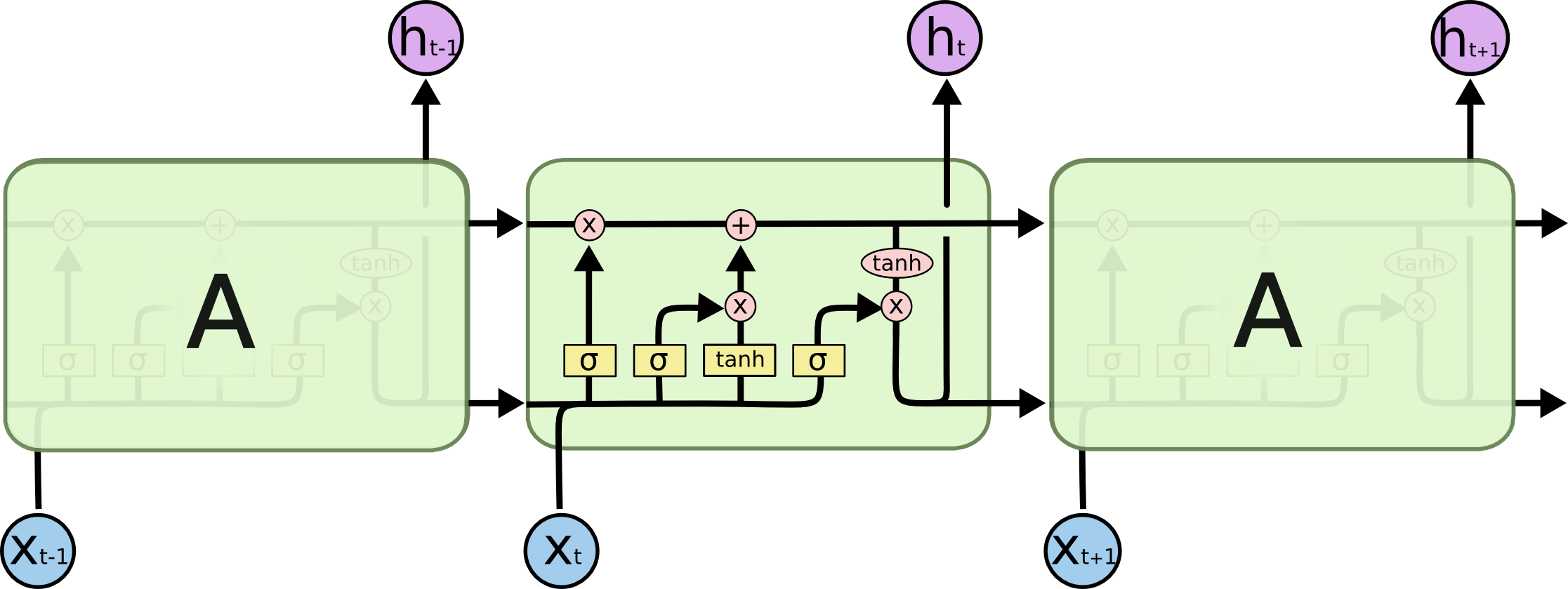
LSTM
下面以LSTM层中只有一个神经元为例(units=1),说明前向传播过程。下面的ot,ht,ct都是一维的。如果units不只一个,则每个神经元均按照如下方式计算,可类比一个全连接层有一个和多个神经元,同一层的这些神经元之间是没有联系的。
前向传播:
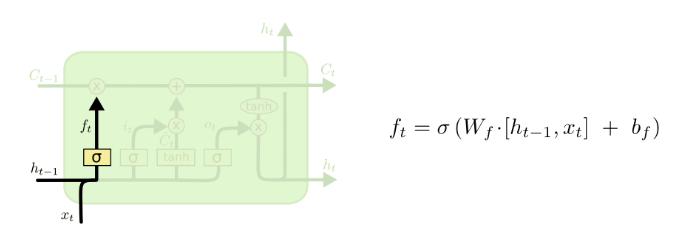
 输入:本次输入X(t),神经元的上一个状态C(t-1),神经元的上一个隐藏状态H(t-1)
输入:本次输入X(t),神经元的上一个状态C(t-1),神经元的上一个隐藏状态H(t-1)
输出:本次更新后的神经元状态C(t),本次的隐藏状态H(t)
计算详述:
遗忘门计算:
输入门与本次计算状态:
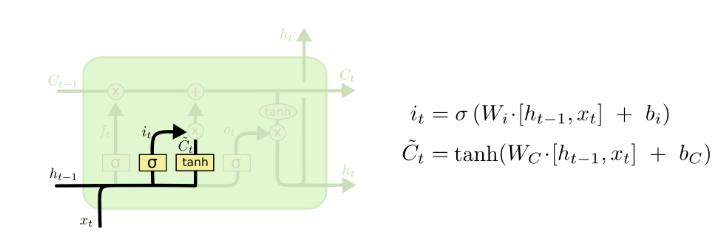
状态更新计算:
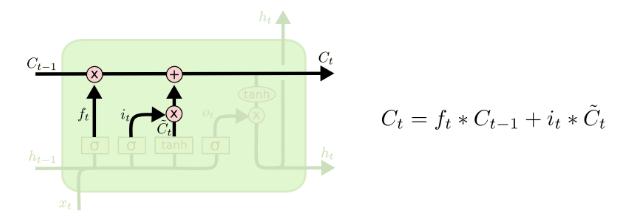
输出门与输出计算:
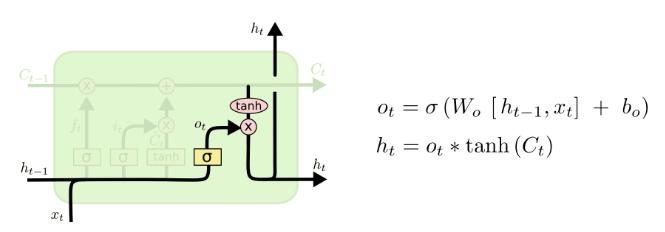
tensorflow的实现:
def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Run one step of LSTM.
Args:
inputs: input Tensor, must be 2-D, `[batch, input_size]`.
state: if `state_is_tuple` is False, this must be a state Tensor,
`2-D, [batch, state_size]`. If `state_is_tuple` is True, this must be a
tuple of state Tensors, both `2-D`, with column sizes `c_state` and
`m_state`.
Returns:
A tuple containing:
- A `2-D, [batch, output_dim]`, Tensor representing the output of the
LSTM after reading `inputs` when previous state was `state`.
Here output_dim is:
num_proj if num_proj was set,
num_units otherwise.
- Tensor(s) representing the new state of LSTM after reading `inputs` when
the previous state was `state`. Same type and shape(s) as `state`.
Raises:
ValueError: If input size cannot be inferred from inputs via
static shape inference.
"""
num_proj = self._num_units if self._num_proj is None else self._num_proj
sigmoid = math_ops.sigmoid
if self._state_is_tuple: # 通常都是走这个条件
(c_prev, m_prev) = state
else: # 几乎不会走到这儿
c_prev = array_ops.slice(state, [0, 0], [-1, self._num_units])
m_prev = array_ops.slice(state, [0, self._num_units], [-1, num_proj])
input_size = inputs.get_shape().with_rank(2)[1]
if input_size.value is None:
raise ValueError("Could not infer input size from inputs.get_shape()[-1]")
# i = input_gate, j = new_input, f = forget_gate, o = output_gate
lstm_matrix = math_ops.matmul(
array_ops.concat([inputs, m_prev], 1), self._kernel)
lstm_matrix = nn_ops.bias_add(lstm_matrix, self._bias)
i, j, f, o = array_ops.split(
value=lstm_matrix, num_or_size_splits=4, axis=1)
# Diagonal connections
if self._use_peepholes:
c = (sigmoid(f + self._forget_bias + self._w_f_diag * c_prev) * c_prev +
sigmoid(i + self._w_i_diag * c_prev) * self._activation(j))
else:
c = (sigmoid(f + self._forget_bias) * c_prev + sigmoid(i) *
self._activation(j))
if self._cell_clip is not None:
# pylint: disable=invalid-unary-operand-type
c = clip_ops.clip_by_value(c, -self._cell_clip, self._cell_clip)
# pylint: enable=invalid-unary-operand-type
if self._use_peepholes:
m = sigmoid(o + self._w_o_diag * c) * self._activation(c)
else:
m = sigmoid(o) * self._activation(c)
if self._num_proj is not None:
m = math_ops.matmul(m, self._proj_kernel)
if self._proj_clip is not None:
# pylint: disable=invalid-unary-operand-type
m = clip_ops.clip_by_value(m, -self._proj_clip, self._proj_clip)
# pylint: enable=invalid-unary-operand-type
new_state = (LSTMStateTuple(c, m) if self._state_is_tuple else
array_ops.concat([c, m], 1))
return m, new_state
手动实现,训练设置:tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(lstm_dim)
最终训练结果bias=0,所以自己手动实现解析的时没有考虑bias
import numpy as np
import math
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.power(math.e, -1 * x))
class LSTMCell:
def __init__(self, kernel):
self.kernel = kernel
self.forget_bias = 1.0
def __call__(self, seqs, *args, **kwargs):
fw = []
h_zero_state = np.zeros(shape=[1, self.kernel.shape[1] // 4], dtype=float)
c_zero_state = np.zeros(shape=[1, self.kernel.shape[1] // 4], dtype=float)
for index in range(seqs.shape[0]):
combine_input = np.concatenate(([seqs[index]], h_zero_state), axis=-1)
lstm_matrix = np.matmul(combine_input, self.kernel)
i, j, f, o = np.split(lstm_matrix, indices_or_sections=4, axis=1)
c = sigmoid(f + self.forget_bias) * c_zero_state + sigmoid(i) * np.tanh(j)
m = sigmoid(o) * np.tanh(c)
fw.append(m)
c_zero_state = c
h_zero_state = m
return fw
LSTM的反向传播
其他变种
参考文献:http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/
Bi-LSTM
DEMO
使用keras的循环层的时候,如果循环层是最外层,那么循环层的input shape的第一个维度为seq_length。如果不是最外层,第一个维度为序列中每个数据的shape
# coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
tf.enable_eager_execution()
x = np.linspace(-100, 100, 1000)
y = np.sin(x)
time_step = 50
def to_train_label(serial, time_step=50):
inputs = []
out = []
for i in range(serial.shape[0] - time_step - 1):
inputs.append(serial[i:i + time_step])
out.append(serial[i + time_step])
return np.array(inputs), np.array(out)
input_data, label = to_train_label(y, time_step)
input_data = tf.expand_dims(input_data, 2)
label = tf.expand_dims(label, 1)
print(input_data.shape, label.shape)
input = tf.keras.Input(shape=[time_step, 1])
rnn = tf.keras.layers.LSTM(units=128, input_shape=[1, ])(input)
out = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=1)(rnn)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=input, outputs=out)
model.compile(optimizer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(), loss='mean_squared_error')
model.fit(input_data, label, batch_size=512, epochs=50)
model.save("../model/my.h5")
start = np.expand_dims(input_data.numpy()[-1], 0).copy()
pres = []
for i in range(50):
next = model.predict(start)
start[0, :time_step - 1] = start[0, 1:]
start[0, time_step - 1] = next
pres.append(next[0][0])
last = np.ndarray.flatten(input_data.numpy()[-1])
all = np.concatenate((last, pres))
plt.plot(list(range(len(all))), all)
plt.show()
print(all)
应用
参考文献
https://cairohy.github.io/2017/06/05/ml-coding-summarize/Tensorflow%E7%9A%84RNN%E5%92%8CAttention%E7%9B%B8%E5%85%B3/

Comments